Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: A Comprehensive Guide
A Comprehensive Guide To Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: Tackle Parasitic Control In Animals Effectively
Editor's Notes:
Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: A Comprehensive Guide For Parasitic Control In Animals have published today, 20th June 2023, after lots of hard work. Ivermectin and Fenbendazole are two of the most widely used antiparasitic drugs in veterinary medicine. They are effective against a broad spectrum of parasites, including gastrointestinal nematodes, lungworms, and ectoparasites such as lice and mites. This guide will provide you with all the information you need to know about Ivermectin and Fenbendazole, including their uses, dosages, side effects, and contraindications.
We understand that dealing with parasites in animals can be a real pain. That's why we've done all the hard work for you and put together this comprehensive guide to Ivermectin and Fenbendazole. So, whether you're a veterinarian, a farmer, or just a pet owner, this guide has something for you.
Key Differences Between Ivermectin And Fenbendazole:
| Feature | Ivermectin | Fenbendazole |
|---|---|---|
| Spectrum of activity | Broad spectrum | Narrow spectrum |
| Dosage | 0.2 mg/kg | 5-10 mg/kg |
| Side effects | Rare | More common |
| Contraindications | None | Pregnant animals |
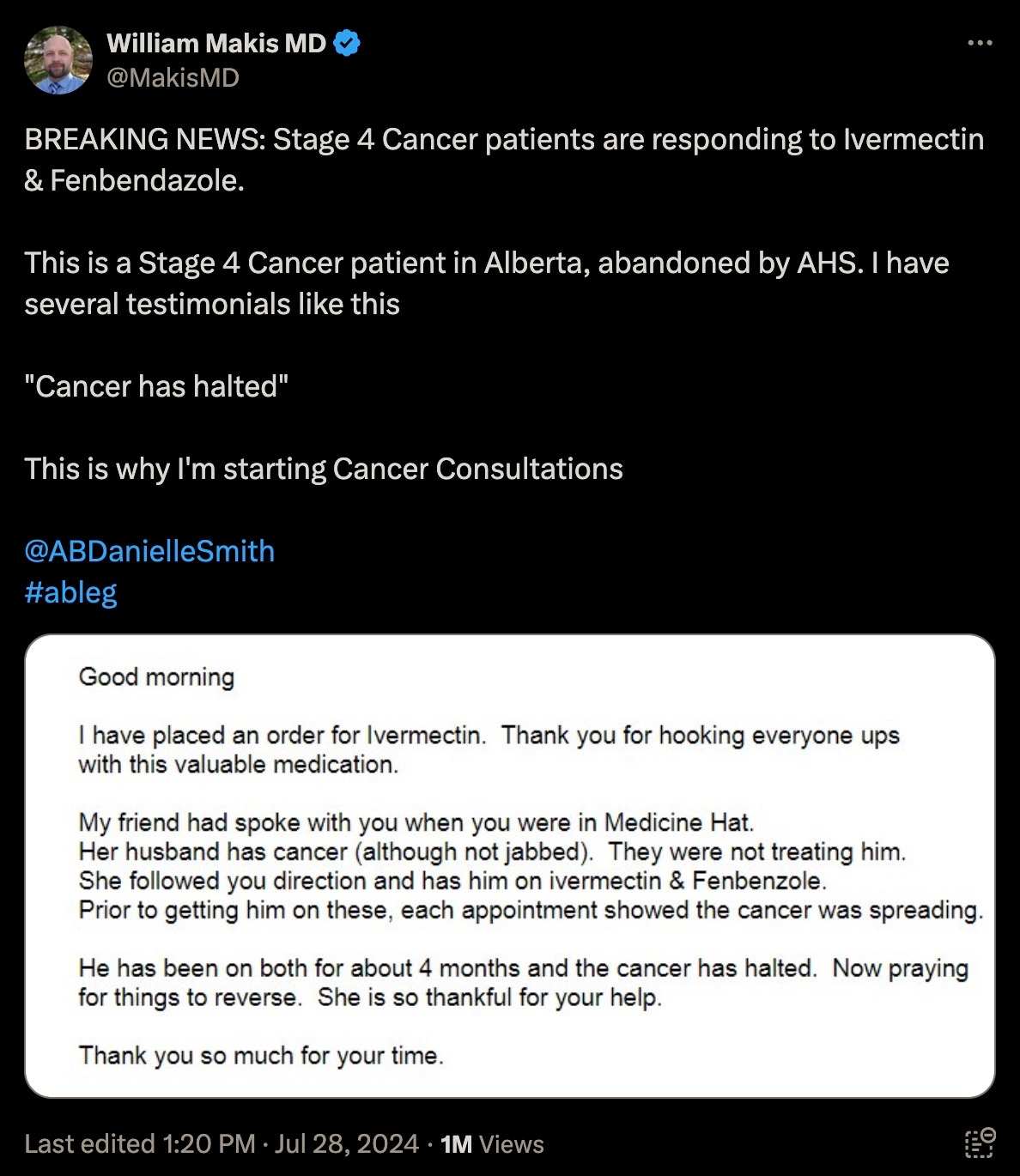
Stage 4 Cancer patients responding to Ivermectin & Fenbendazole | The - Source stuartbramhall.wordpress.com
Ivermectin
Ivermectin is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic drug that is effective against a wide range of parasites, including gastrointestinal nematodes, lungworms, and ectoparasites such as lice and mites. It is a safe and effective drug that has been used in veterinary medicine for over 30 years.
Fenbendazole
Fenbendazole is a narrow-spectrum antiparasitic drug that is effective against gastrointestinal nematodes. It is less effective against lungworms and ectoparasites. Fenbendazole is a safe and effective drug that has been used in veterinary medicine for over 20 years.
Choosing The Right Drug
The best drug for your animal will depend on the type of parasite that is causing the infection. If you are not sure what type of parasite your animal has, you should consult with a veterinarian.
Dosage
The dosage of Ivermectin or Fenbendazole will depend on the weight of your animal. It is important to follow the dosage instructions on the product label carefully.
Side Effects
Ivermectin and Fenbendazole are generally safe and well-tolerated drugs. However, some side effects can occur, such as gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, and vomiting. These side effects are usually mild and will go away within a few days.
Contraindications
Ivermectin and Fenbendazole are not safe for use in all animals. Ivermectin should not be used in animals that are sensitive to the drug. Fenbendazole should not be used in pregnant animals.
Conclusion
Ivermectin and Fenbendazole are two of the most effective antiparasitic drugs available for veterinary use. They are safe and effective drugs that can be used to treat a wide range of parasitic infections. By following the information in this guide, you can choose the right drug for your animal and ensure that they receive the best possible care.
FAQ
This section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions regarding the use of Ivermectin and Fenbendazole for parasitic control in animals.
Question 1: Are Ivermectin and Fenbendazole safe for all animals?
No, these drugs are not suitable for all animals. Ivermectin can be toxic to certain breeds of dogs, cats, rabbits, and other sensitive species. Fenbendazole should not be administered to pregnant or lactating animals.

Ivermectin Injection - Source www.montagelabs.com
Question 2: How often should Ivermectin and Fenbendazole be administered?
The frequency of administration depends on the parasite being targeted, the animal's species, and its environment. Consult a veterinarian for a tailored treatment schedule.
Question 3: Can Ivermectin and Fenbendazole be used together?
Yes, these drugs can be used concurrently for broad-spectrum parasitic control. However, always consult a veterinarian for proper dosing and potential interactions.
Question 4: What are the potential side effects of Ivermectin and Fenbendazole?
Side effects vary depending on the animal and dosage. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, neurological signs, and, in rare cases, liver damage.
Question 5: Can I use Ivermectin and Fenbendazole for humans?
No, these drugs are not approved for human use. They can cause severe side effects in humans and should only be used under strict veterinary supervision for animals.
Question 6: Are there any alternatives to Ivermectin and Fenbendazole?
Yes, there are other medications available for parasitic control. Consult a veterinarian to determine the most appropriate option for your animal.
Remember, proper use of Ivermectin and Fenbendazole requires veterinary guidance to ensure effectiveness and minimize risks. Always follow the prescribed dosage and schedule, and consult a veterinarian promptly if any side effects are observed.
Moving on, let's explore other important aspects of parasitic control in animals...
Tips For Effective Ivermectin and Fenbendazole Administration
Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: A Comprehensive Guide For Parasitic Control In Animals
Tip 1: Follow Dosage Instructions Carefully: Determine the correct dosage based on the animal's weight and consult with a veterinarian for personalized guidance. Overdosing can be harmful, while underdosing may render the treatment ineffective.
Tip 2: Ensure Correct Administration: Administer the medication orally, as directed by the veterinarian. Avoid mixing it with feed or water, as this can affect its absorption and efficacy.
Use proper dosing equipment, such as a syringe or dosing gun, to ensure accurate measurement and administration.
Tip 3: Plan Treatment Frequency: Establish a regular treatment schedule based on the veterinarian's recommendations. This will help prevent re-infestation and ensure ongoing protection against parasites.
Adhere to the recommended treatment intervals, as skipping doses can jeopardize the effectiveness of the medication.
Tip 4: Monitor Animals for Adverse Reactions: Although ivermectin and fenbendazole are generally safe, monitor animals for any adverse reactions, especially after the first dose. Signs to watch for include vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and lethargy.
Report any unusual symptoms to the veterinarian promptly.
Tip 5: Store Medications Properly: Store ivermectin and fenbendazole in a cool, dry place out of reach of children and animals. Moisture, heat, and direct sunlight can affect their potency and stability.
Follow the storage instructions provided on the medication label carefully.
Summary: Adhering to these tips ensures effective parasitic control, minimizes the risk of side effects, and supports the overall health and well-being of animals. Consult with a qualified veterinarian for personalized guidance and to address any specific concerns.
For more comprehensive information, refer to Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: A Comprehensive Guide For Parasitic Control In Animals
Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: A Comprehensive Guide For Parasitic Control In Animals
Effective parasitic control in animals is critical for their health and well-being. Ivermectin and fenbendazole are two widely used anthelmintics that play a crucial role in this regard. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of these medications, exploring their mechanisms of action, spectrum of activity, dosage recommendations, and potential side effects.
- Anthelmintic drugs: Ivermectin and fenbendazole belong to the class of drugs known as anthelmintics, which are specifically designed to combat parasitic worms.
- Broad-spectrum: Ivermectin exhibits a broad spectrum of activity against a wide range of internal parasites, including roundworms, lungworms, and certain types of mites.
- Nematodes: Fenbendazole is particularly effective against nematodes, which are roundworms that can infest the gastrointestinal tract of animals.
- Dosage: The dosage of ivermectin and fenbendazole varies depending on the species of animal, its weight, and the severity of the parasitic infection.
- Safety profile: Both ivermectin and fenbendazole are generally considered safe for use in animals, but they can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal upset, neurological symptoms, and allergic reactions in some cases.
- Veterinary consultation: It is crucial to consult with a veterinarian before administering ivermectin or fenbendazole to animals, as they can provide guidance on the appropriate dosage and potential interactions with other medications.
Understanding these key aspects of ivermectin and fenbendazole is essential for effective parasitic control in animals. Proper use of these medications, in conjunction with good hygiene practices and regular veterinary checkups, can help prevent parasitic infections and maintain the health and well-being of animals.

Animal drug ivermectin and COVID: Poison center calls up, stores out - Source eu.usatoday.com

High Quality Animal Medicine Veterinary Drugs: Including Fenbendazole - Source cxbt-showvet.en.made-in-china.com
Ivermectin And Fenbendazole: A Comprehensive Guide For Parasitic Control In Animals
Ivermectin and fenbendazole are two of the most commonly used drugs for the control of parasites in animals. Both drugs are effective against a wide range of parasites, including roundworms, tapeworms, and flukes. Ivermectin is also effective against some types of mites and lice.

FISH AID ANTIBIOTICS Fenbendazole Fish Anti-Parasitic Treatment, 3 - Source www.chewy.com
Ivermectin is a macrocyclic lactone that works by binding to glutamate-gated chloride channels in the parasite's nervous system. This binding causes the channels to open, which leads to an influx of chloride ions into the parasite's cells. The increased chloride concentration causes the parasite's muscles to relax, which leads to paralysis and death. Fenbendazole is a benzimidazole that works by binding to tubulin, a protein that is essential for the formation of microtubules. Microtubules are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell division and intracellular transport. Fenbendazole's binding to tubulin disrupts these processes, which leads to the death of the parasite.
Both ivermectin and fenbendazole are safe for use in a wide variety of animals, including cattle, sheep, goats, swine, and horses. However, there are some potential side effects that should be considered. Ivermectin can cause neurological side effects, such as tremors, ataxia, and seizures. Fenbendazole can cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and vomiting.
Ivermectin and fenbendazole are essential drugs for the control of parasites in animals. However, it is important to use these drugs responsibly and to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
| Drug | Mechanism of action | Side effects |
|---|---|---|
| Ivermectin | Binds to glutamate-gated chloride channels in the parasite's nervous system | Neurological side effects, such as tremors, ataxia, and seizures |
| Fenbendazole | Binds to tubulin, a protein that is essential for the formation of microtubules | Gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea and vomiting |
Conclusion
Ivermectin and fenbendazole are two of the most important drugs for the control of parasites in animals. Both drugs are safe and effective, but there are some potential side effects that should be considered. It is important to use these drugs responsibly and to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
The use of ivermectin and fenbendazole has helped to improve the health and productivity of animals around the world. These drugs have also helped to reduce the transmission of parasitic diseases to humans.